18+ Plantar Fascia Anatomy
They are innervated by the medial or lateral plantar nerves which are branches of the tibial nerve. The fascia is thick centrally known as aponeurosis and is.

Pin Em Medical Msk
While the pathophysiology is not completely understood recent evidence suggests that plantar fasciitis is due to a disruption in normal biomechanics that results in repetitive small tears.

. Web Description The Plantar aponeurosis is the modification of Deep fascia which covers the sole. Plantar fasciitis PLAN-tur fas-e-I-tis is one of the most common causes of heel pain. These fibers are mostly longitudinal but also transverse.
The pain is often most severe after long periods of rest. Web The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis is a dense collection of collagen fibers on the sole plantar surface of the foot. The calcaneus is the largest of all the tarsals and the largest bone in the foot.
Medial compartment of the sole - covered by the medial plantar fascia. Web Fascia can be classified as superficial deep visceral or parietal and further classified according to anatomical location. Web The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis forms part of the deep fascia of the sole of the foot and provides a strong mechanical linkage between the calcaneus and the toes.
Web Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the fibrous tissue plantar fascia along the bottom of your foot that connects your heel bone to your toes. Web Anatomy of the Plantar Fascia. Pain when you stand up after sleeping or sitting down.
Web Plantar fasciitis presents as sharp unilateral pain at the proximal plantar aspect of the foot. Arising predominantly from the calcaneal tuberosity the plantar fascia attaches distally through several slips to the plantar aspect of the forefoot as well as the. Web Plantar Flexion vs.
Web The plantar fascia or plantar aponeurosis 1 is the thick connective tissue aponeurosis which supports the arch on the bottom plantar side of the foot. Anatomy The plantar fascia is a long thin ligament that lies directly beneath the skin on the bottom of your foot. They act collectively to stabilise the arches of the foot and individually to control movement of the digits.
Web Anatomy by Chris Mallac. The pain usually goes away after walking for a few minutes. Benjamin 2009 that is one of the most common causes of heel pain.
Web Anatomy The calcaneus is one of seven tarsal bones that make up the foot. 3 4 7 Distally at the metatarsophalangeal joints it. Both are important for engaging the tendons muscles and ligaments in the lower leg ankles and feet.
Web Plantar fasciitis occurs when the plantar fascia a strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed. Web Clinically Relevant Anatomy The plantar fascia Comprised of white longitudinally organized fibrous connective tissue which originates on the periosteum of the medial calcaneal tubercle where it is thinner but it extends into a thicker central portion. They are all innervated by the lateral plantar nerve S1-S2 a branch of the tibial nerve.
It accounts for 1 of all orthopedic visits Riddle Schappert 2004. Central compartment of the sole invests by the dense plantar aponeurosis. The lateral compartment of the sole covered by the thinner lateral plantar fascia.
Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament spring ligament. Plantar fasciitis can be caused by a number of factors including type of shoes foot structure overuse and types of walking surfaces. Some types of pain you might feel include.
Practice Essentials Plantar fasciitis is the pain caused by degenerative irritation at the insertion of. Dorsiflexion is the opposite flexing your foot so that your toes move toward your body. Craig C Young MD more.
The pain can change depending on what youre doing or the time of day. There are ten intrinsic muscles located in the plantar aspect sole of the foot. Web Plantar Aspect.
Craig C Young MD. Runs underneath your foot from the heel to the base of your toes. Chris Mallac identifies the unique anatomical and biomechanical features of the plantar fascia describes the pathogenesis and clinical presentation of rupture and how this injury may be managed in the athlete.
Web Overview What is fascia. Fascia is the band of thin fibrous connective tissue that wraps around and supports every structure in your body. Superficial fascia is found directly under the skin and superficial adipose layers.
Web Lateral plantar muscles inferior view The lateral chamber formed by the plantar fascia contains three muscles. A strong ligament that connects bones in the ankle and foot gives your arch structure and helps support your body weight. Web The plantar fascia PF also known as the plantar aponeurosis originates proximally at the medial tubercle of the distal calcaneus and broadens as it extends distally Figure 1.
All of the tarsals are considered short bones. It can show stratification both grossly and microscopically. Plantar flexion is the movement of pointing your toes away from your body.
Web Plantar fasciitis usually causes an achy pain in your heel or along the bottom of your foot. It is a thick connective tissue that functions to support and protect the underlying vital structures of the foot. Their muscle bellies form the surface of the lateral foot sole ball of the little toe.
Medial plantar heel pain is a common overuse injury in running based athletes or in those who stand on their. The main symptom of plantar fasciitis is heel pain. The plantar fascia is a complex structure that extends from the medial calcaneal tubercle the heel bone to the proximal phalanges of the toes the bone at the base of the toe at the metatarsophalangeal MTP joints.
Web The plantar fascia PF can undergo a form of pathological degeneration called plantar fasciitis Lemont et al. Web What You Need to Know Plantar fasciitis is the inflammation of the plantar fascia tissue in the foot used during walking and foot movement. Gross anatomy Posteriorly it attaches to the medial process of the tuberosity of the calcaneus proximal to flexor digitorum brevis.
Plantar fasciitis can cause intense heel pain. Mar 23 2023 Author. Web deep fasciae of the foot divide the sole into three compartments which are.
Web Plantar fascia ligament. Scientists initially thought fascia only provided support to your organs muscles and bones. The calcaneus is a short bone a type of bone meaning that it is about as long as it is wide.
Recent studies suggest that the plantar fascia is actually an aponeurosis rather than true fascia.

Anatomy Of The Plantar Aspect Of The Foot Demonstrating The Bands Of Download Scientific Diagram
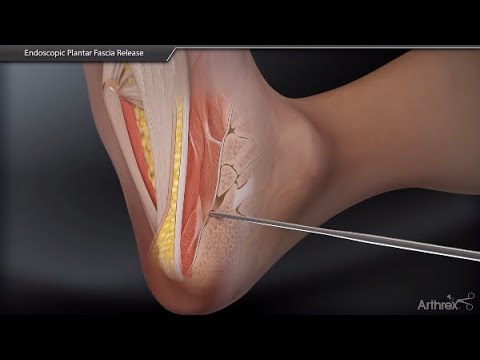
Plantar Fascia The Most Up To Date Encyclopedia News Review Research

Anatomy Of Plantar Fascia

What Is Plantar Fasciitis Anatomy Symptoms Risk Factors Diagnosis Treatment Youtube
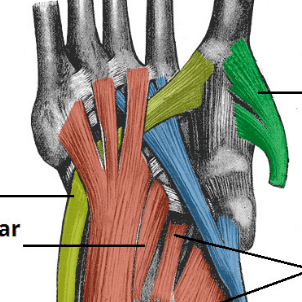
Plantar Fasciitis Clinical Features Management Teachmesurgery
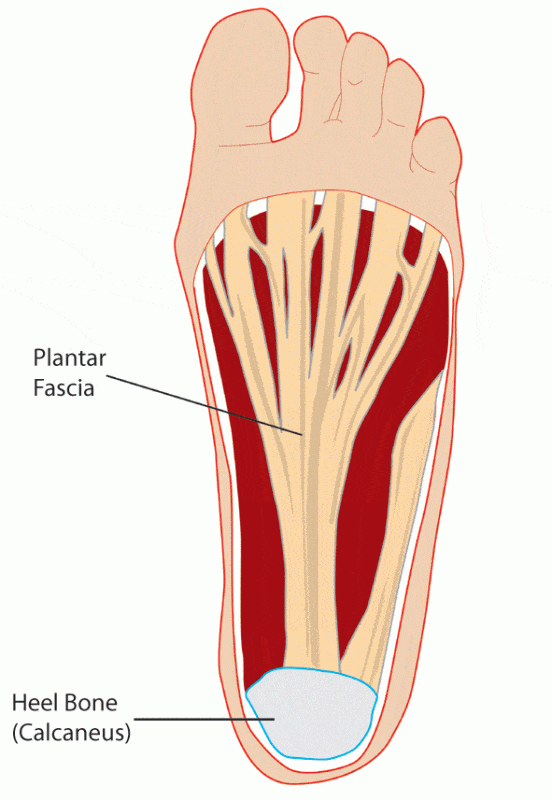
Plantar Fascia Anatomy Docpods

Healthy Street Deep Fascia Of Foot The Deep Fascia Of The Dorsum Of The Foot Is Thin Where It Is Continuous Proximally With The Inferior Extensor Retinaculum Over The Lateral

Plantar Fascia Wikipedia
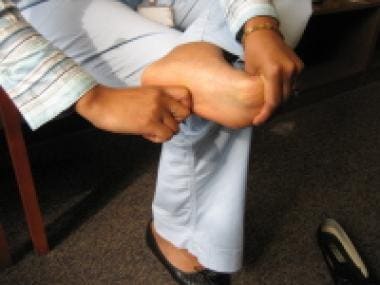
Plantar Fasciitis Practice Essentials Anatomy Pathophysiology
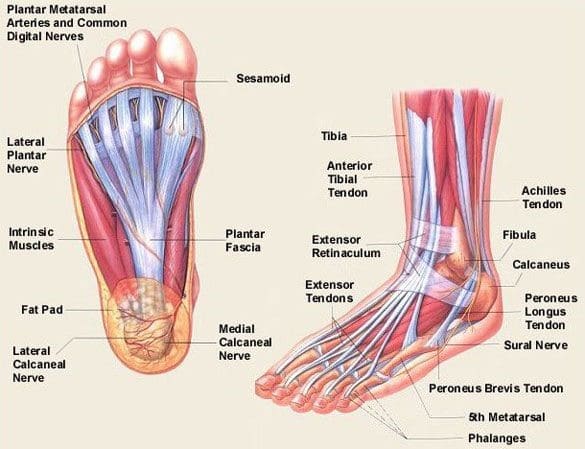
Cause Of Plantar Fasciitis Pivotal Motion Physiotherapy
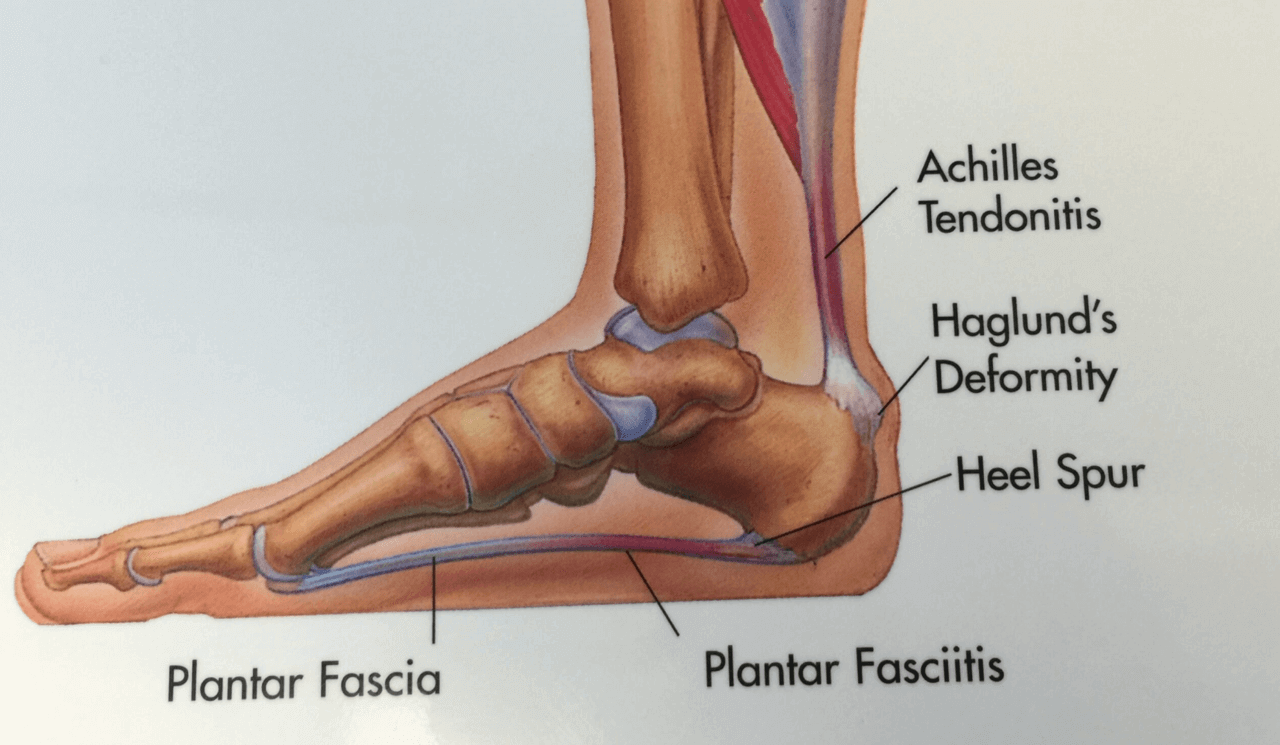
Seattle Bellevue Heel Pain Center Issaquah Foot Ankle Specialists

Plantar Fasciitis Anatomy And Why You Need To Know It
Plantar Fasciitis Joint Pain Info

Tens Unit For Plantar Fasciitis Tens Units

The Plantar Fascia Is A Thick Band Of Connective Tissue That Supports Download Scientific Diagram
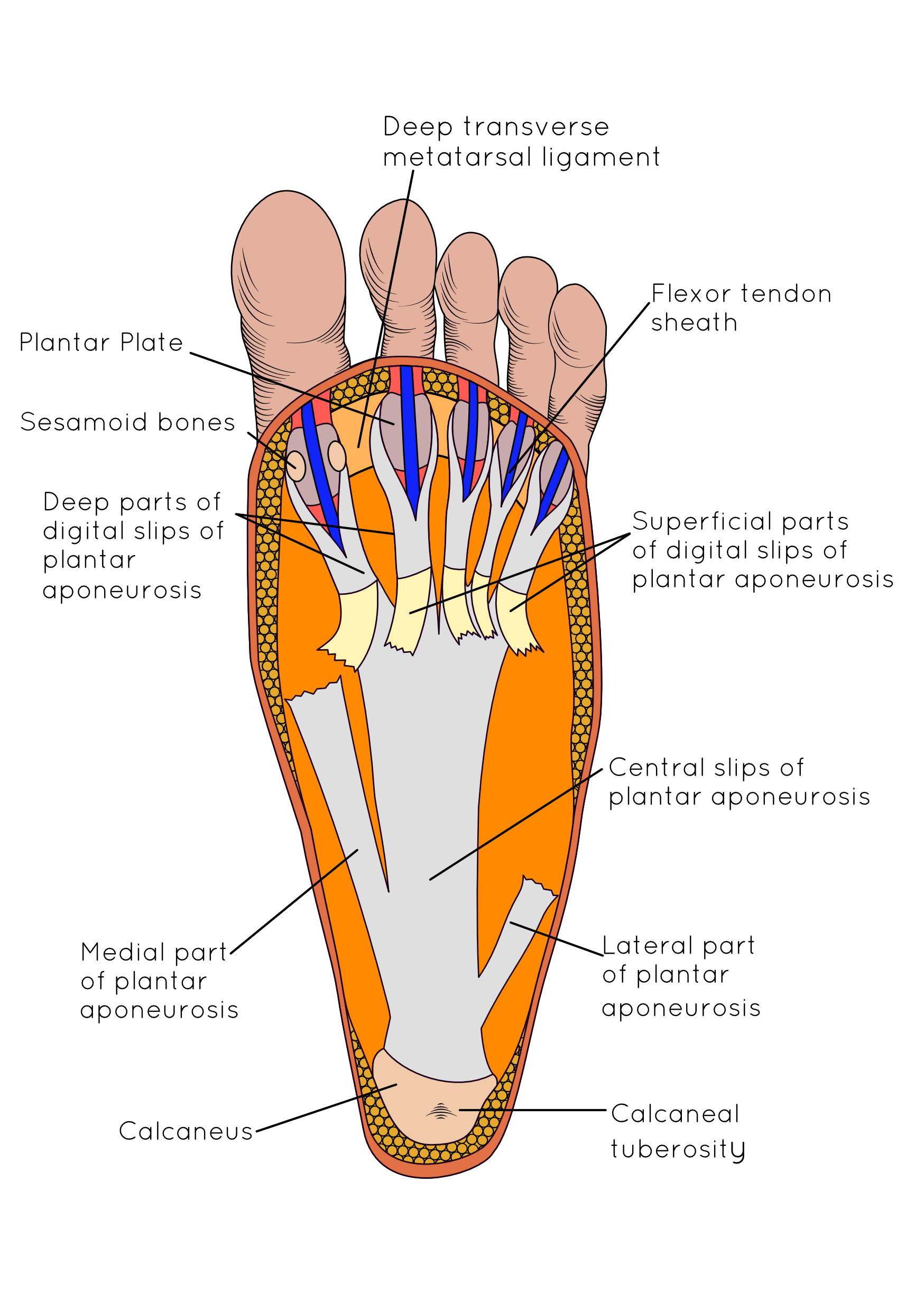
Plantar Fasciitis In Runners A Pain In The Heel Insoles And Orthotics Healthy Step

The Plantar Fascia Enthesis